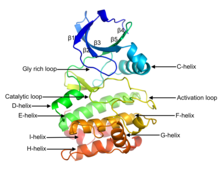
Protein kinase domain
[6] Protein kinase function has been evolutionarily conserved from Escherichia coli to Homo sapiens.
Protein kinases play a role in a multitude of cellular processes, including division, proliferation, apoptosis, and differentiation.
[9] Humans have only 437 kinase domains that have catalytic activity; the rest are pseudokinases or catalyze other reactions.
The catalytic loop includes the "HRD motif" (for the amino acid sequence His-Arg-Asp), whose aspartic acid residue interacts directly with the hydroxyl group of the target serine, threonine, or tyrosine residue that is phosphorylated.
Broadly, the state or conformation of the kinase may be classified as DFGin or DFGout, depending on whether the Asp residue of the DFG motif is in or out of the active site.