Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src
c-Src was originally discovered by American scientists J. Michael Bishop and Harold E. Varmus, for which they were awarded the 1989 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.
[7] In 1979, J. Michael Bishop and Harold E. Varmus discovered that normal chickens possess a gene that is structurally closely related to v-Src.
Eventually this normal gene mutated into an abnormally functioning oncogene within the Rous sarcoma virus.
There are 9 members of the Src family kinases: c-Src, Yes, Fyn, Fgr, Yrk, Lyn, Blk, Hck, and Lck.
Src contains at least three flexible protein domains, which, in conjunction with myristoylation, can mediate attachment to membranes and determine subcellular localization.
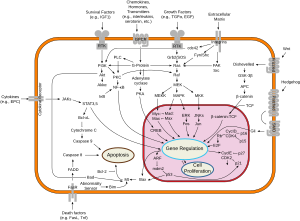
[23] Since the activation of c-Src leads to the promotion of survival, angiogenesis, proliferation and invasion pathways, the aberrant growth of tumors in cancers is observed.
Researchers have shown that Src expression is 5 to 8 fold higher in premalignant polyps than normal mucosa.
[29][30][31] Overexpression of Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 (HER2), also known as erbB2, is correlated with a worse prognosis for breast cancer.
Other tyrosine kinase inhibitor drugs that are in clinical trials include bosutinib,[38] bafetinib, Saracatinib(AZD-0530), XLl-999, KX01 and XL228.
[6] HSP90 inhibitor NVP-BEP800 has been described to affect stability of Src tyrosine kinase and growth of T-cell and B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemias.