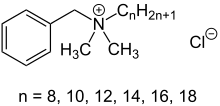
Quaternary ammonium cation
Quats are used in consumer applications including as antimicrobials (such as detergents and disinfectants), fabric softeners, and hair conditioners.
Industrial production of commodity quat salts usually involves hydrogenation of fatty nitriles, which can generate primary or secondary amines.
Quaternary ammonium cations containing N−C−C−H units can also undergo the Hofmann elimination and Emde degradation.
A subject of concern is the potential effect of increased use of quats related to COVID-19 pandemic on antibiotic resistance in a larger microbial community in nature and engineered environment.
)[22] Quaternary ammonium compounds are lethal to a wide variety of organisms except endospores and non-enveloped viruses, both having no accessible membrane coat to attack.
[22] In organic chemistry, quaternary ammonium salts are employed as phase transfer catalysts (PTCs).
The highly reactive reagent dichlorocarbene is generated via PTC by reaction of chloroform and aqueous sodium hydroxide.
[26] Characteristically, the cations contain one or two long alkyl chains derived from fatty acids linked to an ethoxylated ammonium salt.
Lesser effects are seen in reductions of leaf expansion, resulting in thicker leaves with darker green color.
For example, phosphatidylcholines, a major component of biological membranes, are a member of the lecithin group of fatty substances in animal and plant tissues.
[citation needed] Quaternary ammonium compounds can display a range of health effects, amongst which are mild skin and respiratory irritation [37] up to severe caustic burns on skin and the gastrointestinal wall (depending on concentration), gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g., nausea and vomiting), coma, convulsions, hypotension and death.
[38] They are thought to be the chemical group responsible for anaphylactic reactions that occur with use of neuromuscular blocking drugs during general anaesthesia in surgery.
[40] Quaternary ammonium-based disinfectants (Virex and Quatricide) were tentatively identified as the most probable cause of jumps in birth defects and fertility problems in caged lab mice.
[43] The studies contradict earlier toxicology data reviewed by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (U.S. EPA) and the EU Commission.