Reactive-ion etching
Gas enters through small inlets in the top of the chamber, and exits to the vacuum pump system through the bottom.
In this system, the ICP is employed as a high density source of ions which increases the etch rate, whereas a separate RF bias is applied to the substrate (silicon wafer) to create directional electric fields near the substrate to achieve more anisotropic etch profiles.
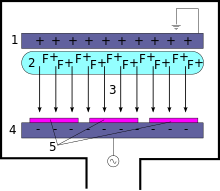
[2] Plasma is initiated in the system by applying a strong RF (radio frequency) electromagnetic field to the wafer platter.
The oscillating electric field ionizes the gas molecules by stripping them of electrons, creating a plasma.
Because of the large voltage difference, the positive ions tend to drift toward the wafer platter, where they collide with the samples to be etched.
Etch conditions in an RIE system depend strongly on the many process parameters, such as pressure, gas flows, and RF power.