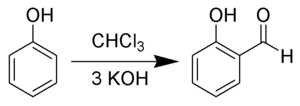
Reimer–Tiemann reaction
This interaction favors selective ortho-formylation, consistent with other electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions.
Hydroxides are not readily soluble in chloroform, thus the reaction is generally carried out in a biphasic solvent system.
In the simplest sense this consists of an aqueous hydroxide solution and an organic phase containing the chloroform.
This can be achieved by rapid mixing, phase-transfer catalysts, or an emulsifying agent such as 1,4-dioxane as solvent.
Using carbon tetrachloride instead of chloroform gives a carboxylic acid product instead of an aldehyde.