Self-determination
[18] Thomas Jefferson further promoted the notion that the will of the people was supreme, especially through authorship of the United States Declaration of Independence, which became an inspiration for European nationalist movements during the 19th century.
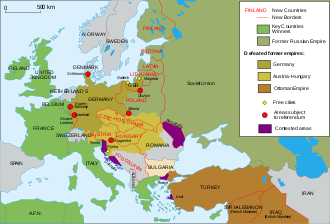
[13] The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk in March 1918 led to Soviet Russia's exit from the war and the nominal independence of Armenia, Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Ukraine, Lithuania, Georgia and Poland, though in fact those territories were under German control.
[27] One of the German objections to the Treaty of Versailles was a somewhat selective application of the principle of self-determination, as the Republic of German-Austria, which included the Sudetenland, was seen as representing the will to join Germany in those regions, while the majority of people in Danzig wanted to remain within the Reich.
The Statute of Westminster granted independence to Canada, New Zealand, Newfoundland, Australia, and the Union of South Africa after the British parliament declared itself incapable of passing laws over them without their consent.
Japan went to considerable trouble to argue that Manchukuo was justified by the principle of self-determination, claiming that people of Manchuria wanted to break away from China and asked the Kwantung Army to intervene on their behalf.
However, the Lytton commission which had been appointed by the League of Nations to decide if Japan had committed aggression or not, stated the majority of people in Manchuria who were Han Chinese who did not wish to leave China.
The ratification of the United Nations Charter in 1945 at the end of World War II placed the right of self-determination into the framework of international law and diplomacy.
Although satellite states were independent and possessed sovereignty, the Soviet Union violated principles of self-determination by suppressing the Hungarian revolution of 1956 and the Prague Spring Czechoslovak reforms of 1968.
[13] In Asia, the Soviet Union had already converted Mongolia into a satellite state but abandoned propping up the Second East Turkestan Republic and gave up its Manchurian claims to China.
[citation needed] In the revolutions of 1989–90, the communist regimes of Soviet satellite states collapsed in rapid succession in Poland, Hungary, Czechoslovakia, East Germany, Bulgaria, Romania, and Mongolia.
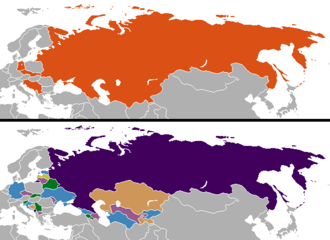
[13] In December 1991, Gorbachev resigned as president and the Soviet Union dissolved relatively peacefully into fifteen sovereign republics, all of which rejected Communism and most of which adopted democratic reforms and free-market economies.
Significant movements for self-determination also persist for locations that lack de facto independence, such as East Turkistan ("Xinjiang"), Kurdistan, Balochistan, Chechnya, and Palestine.
The 2000 United Nations Millennium Declaration failed to deal with these new demands, mentioning only "the right to self-determination of peoples which remain under colonial domination and foreign occupation.
Present international law does not recognize ethnic and other minorities as separate peoples, with the notable exception of cases in which such groups are systematically disenfranchised by the government of the state they live in.
[50] According to the Helsinki Final Act of 1975, the UN, ICJ and international law experts, there is no contradiction between the principles of self-determination and territorial integrity, with the latter taking precedence.
This is justified by reference to Paragraph 6 of UN Resolution 1514(XV), which states that any attempt "aimed at partial or total disruption of the national unity and the territorial integrity of a country is incompatible with the purposes and principles of the Charter".
[50] The Chinese Communist Party followed the Soviet Union in including the right of secession in its 1931 constitution in order to entice ethnic nationalities and Tibet into joining.
Their primary motivations included self-determination, a history of Chinese colonization and oppression in East Turkistan, and a legacy of independence prior to the invasion by China (the Manchu Qing Dynasty).
[93] Historical records dispute Argentina's claims and whilst acknowledging the garrison was expelled note the existing civilian population remained at Port Louis.
[104] Before the United Nations's adoption of resolution 2908 (XXVII) on 2 November 1972, The People's Republic of China vetoed the former British colony of Hong Kong's right to self-determination on 8 March 1972.
Young localist leaders have led numerous protest actions against pro-Chinese policies to raise awareness of social problems of Hong Kong under Chinese rule.
Though it was also established that it is merely a right within existing sovereign states, after all peoples also need territory and a central government to reach sovereignty in international politics.
[105] Zionism is a nationalist ideology founded by Theodor Herzl which claims a right of historic entitlement by descent as a nation, to exercise self-determination for all Jewish people in the region of Palestine/ancient Israel/land of Israel.
To this date the Kashmiris have been faced with numerous human rights violations committed by both India and Pakistan and have yet to gain complete autonomy which they have been seeking through self-determination.
An experience concerned the findings of a United Nations Assessment Team that led the British territories of North Borneo and Sarawak in 1963 to determine whether or not the populations wished to become a part of the new Malaysia Federation.
[114] The United Nation Team's mission followed on from an earlier assessment by the British-appointed Cobbold Commission which had arrived in the territories in 1962 and held hearings to determine public opinion.
As a strategic location in the Middle East, it was subsequently occupied by several major powers, including the empires of the Assyrians, Egyptians and Persians, from whom the island was seized in 333 BC by Alexander the Great.
Although the Lusignan French aristocracy remained the dominant social class in Cyprus throughout the medieval period, the former assumption that Greeks were treated only as serfs on the island is no longer considered by academics to be accurate.
In the two state solution this usually denotes territorial integrity initiatives, such as resisting occupation in the West Bank, annexation efforts in East Jerusalem or freedom of movement along borders, as well the preservation of important sites such as al-Aqsa mosque.
This was given assent by the Scottish Parliament but, as of July 2022, British Prime Minister Boris Johnson has refused to grant the Section 30 powers required to hold another referendum on the argument that both sides accepted beforehand that the 2014 vote would settle the matter for a generation.