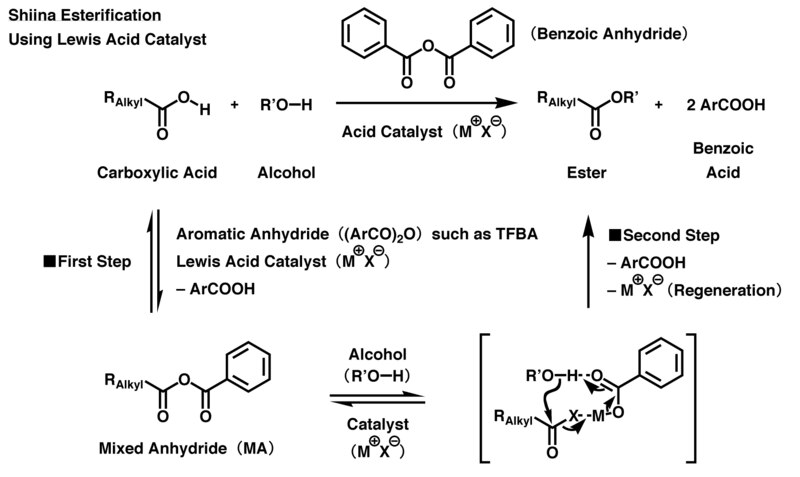
Shiina esterification
The hydroxyl group in the alcohol attacks its host molecule through intermolecular nucleophilic substitution, and at the same time, carboxylate anion, derived from 2-methyl-6-nitrobenzoic acid, acts as a deprotonation agent, promoting the progression of the esterification and producing the desired carboxylic ester.
Because the nucleophilic catalyst is reproduced at the end of the reaction, only small stoichiometric quantities are required.
All of the processes of Shiina esterification consist of reversible reactions, with the exception of the last nucleophilic substitution step with alcohol.
Furthermore, aliphatic carboxylic acid anhydride produced via disproportionation of the MA is simultaneously present in the system; thus, it is directly used as a mixture without being separated.
In the Shiina esterification performed under basic conditions, asymmetric synthesis is realized using chiral nucleophilic catalysts.
It is also possible to realize the kinetic resolution of racemic alcohols by modifying the compositions of the reactants, i.e., by forming MA through reactions between achiral carboxylic acid and the appropriate carboxylic acid anhydride; then, by activating the racemic alcohols using the MA, optically active alcohols and optically active carboxylic acid esters can be obtained.