Sliding (motion)
Sliding is a type of motion between two surfaces in contact.
Both types of motion may occur in bearings.
This means that the force of friction always acts on an object in the direction opposite to its velocity (relative to the surface it's sliding on).
Friction may damage or "wear" the surfaces in contact.
The science and technology of friction, lubrication, and wear is known as tribology.
Sliding may occur between two objects of arbitrary shape, whereas rolling friction is the frictional force associated with the rotational movement of a somewhat disclike or other circular object along a surface.
[2] Correspondingly sliding friction typically produces greater sound and thermal bi-products.
One of the most common examples of sliding friction is the movement of braking motor vehicle tires on a roadway, a process which generates considerable heat and sound, and is typically taken into account in assessing the magnitude of roadway noise pollution.
[3] Sliding friction (also called kinetic friction) is a contact force that resists the sliding motion of two objects or an object and a surface.
Where Fk, is the force of kinetic friction.
μk is the coefficient of kinetic friction, and N is the normal force.
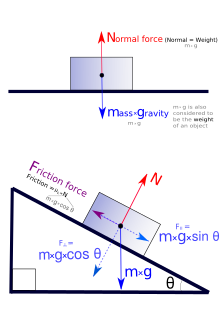
A common problem presented in introductory physics classes is a block subject to friction as it slides up or down an inclined plane.
The component of the force of gravity in the direction of the incline is given by:[4]
The normal force (perpendicular to the surface) is given by:
Therefore, since the force of friction opposes the motion of the block,
To find the coefficient of kinetic friction on an inclined plane, one must find the moment where the force parallel to the plane is equal to the force perpendicular; this occurs when the block is moving at a constant velocity at some angle
is the angle at which the block begins moving at a constant velocity[5]