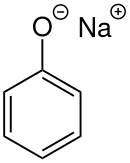
Sodium phenoxide
Solvent-free material is polymeric, each Na center being bound to three oxygen ligands as well as the phenyl ring.
Adducts of sodium phenoxide are molecular, such as the cubane-type cluster [NaOPh]4(HMPA)4.
With acylating agents, one obtains phenyl esters:[citation needed] Sodium phenoxide is susceptible to certain types of electrophilic aromatic substitutions.
For example, it reacts with carbon dioxide to form 2-hydroxybenzoate, the conjugate base of salicylic acid.
[citation needed] Media related to Sodium phenoxide at Wikimedia Commons