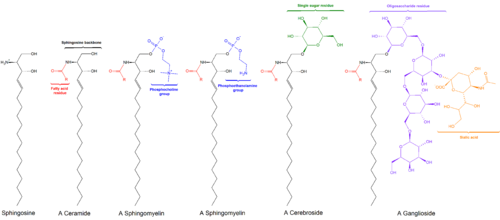
Sphingolipid
Sphingolipids are a class of lipids containing a backbone of sphingoid bases, which are a set of aliphatic amino alcohols that includes sphingosine.
However, studies have demonstrated that serine palmitoyltransferase has some activity toward other species of fatty acyl-CoA[10] and alternative amino acids,[11] and the diversity of sphingoid bases has recently been reviewed.
Dihydrosphingosine is acylated by one of six (dihydro)-ceramide synthase, CerS - originally termed LASS - to form dihydroceramide.
[14] De novo generated ceramide is the central hub of the sphingolipid network and subsequently has several fates.
[16] Sphingolipids are commonly believed to protect the cell surface against harmful environmental factors by forming a mechanically stable and chemically resistant outer leaflet of the plasma membrane lipid bilayer.
[citation needed] Recently, simple sphingolipid metabolites, such as ceramide and sphingosine-1-phosphate, have been shown to be important mediators in the signaling cascades involved in apoptosis, proliferation, stress responses, necrosis, inflammation, autophagy, senescence, and differentiation.
[17][18][19][20][21] Ceramide-based lipids self-aggregate in cell membranes and form separate phases less fluid than the bulk phospholipids.
[22] Sphingolipids are synthesized in a pathway that begins in the ER and is completed in the Golgi apparatus, but these lipids are enriched in the plasma membrane and in endosomes, where they perform many of their functions.
Sphingolipids are virtually absent from mitochondria and the ER, but constitute a 20-35 molar fraction of plasma membrane lipids.
[citation needed] In addition to the important structural functions of complex sphingolipids (inositol phosphorylceramide and its mannosylated derivatives), the sphingoid bases phytosphingosine and dihydrosphingosine (sphinganine) play vital signaling roles in S. cerevisiae.
[citation needed] Sphingolipids have also been implicated with the frataxin protein (Fxn), the deficiency of which is associated with Friedreich's ataxia (FRDA).
Loss of Fxn in the nervous system in mice also activates an iron/sphingolipid/PDK1/Mef2 pathway, indicating that the mechanism is evolutionarily conserved.
[32] Sphingolipids play a key role in neuronal survival in Parkinson's Disease (PD) and their catabolic pathway alteration in the brain is partly represented in cerebrospinal fluid and blood tissues (Table1) and have the diagnostic potential.