Sulfotransferase
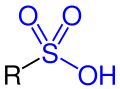
In biochemistry, sulfotransferases (SULTs) are transferase enzymes that catalyze the transfer of a sulfo group (R−SO−3) from a donor molecule to an acceptor alcohol (R−OH) or amine (R−NH2).
[1] The most common sulfo group donor is 3'-phosphoadenosine-5'-phosphosulfate (PAPS).
In the case of alcohol as acceptor, the product is a sulfate (R−OSO−3): whereas an amine leads to a sulfamate (R−NH−SO−3): Both reactive groups for a sulfonation via sulfotransferases may be part of a protein, lipid, carbohydrate or steroid.
[2] The following are examples of sulfotransferases: This biochemistry article is a stub.
You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.