Square root of 3
The square root of 3 is the positive real number that, when multiplied by itself, gives the number 3.
It is more precisely called the principal square root of 3 to distinguish it from the negative number with the same property.
The square root of 3 is an irrational number.
It is also known as Theodorus' constant, after Theodorus of Cyrene, who proved its irrationality.
[citation needed] In 2013, its numerical value in decimal notation was computed to ten billion digits.
[1] Its decimal expansion, written here to 65 decimal places, is given by OEIS: A002194: The fraction
(1.732142857...) can be used as a good approximation.
Despite having a denominator of only 56, it differs from the correct value by less than
, with a relative error of
The rounded value of 1.732 is correct to within 0.01% of the actual value.
[citation needed] The fraction
[citation needed] Archimedes reported a range for its value:
[2] The lower limit
is an accurate approximation for
(six decimal places, relative error
(four decimal places, relative error
It can be expressed as the simple continued fraction [1; 1, 2, 1, 2, 1, 2, 1, …] (sequence A040001 in the OEIS).
: The square root of 3 can be found as the leg length of an equilateral triangle that encompasses a circle with a diameter of 1.
If an equilateral triangle with sides of length 1 is cut into two equal halves, by bisecting an internal angle across to make a right angle with one side, the right angle triangle's hypotenuse is length one, and the sides are of length
The square root of 3 also appears in algebraic expressions for various other trigonometric constants, including[3] the sines of 3°, 12°, 15°, 21°, 24°, 33°, 39°, 48°, 51°, 57°, 66°, 69°, 75°, 78°, 84°, and 87°.
It is the distance between parallel sides of a regular hexagon with sides of length 1.
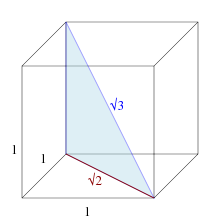
It is the length of the space diagonal of a unit cube.
The vesica piscis has a major axis to minor axis ratio equal to
This can be shown by constructing two equilateral triangles within it.
In power engineering, the voltage between two phases in a three-phase system equals
times the line to neutral voltage.
This is because any two phases are 120° apart, and two points on a circle 120 degrees apart are separated by
times the radius (see geometry examples above).
[citation needed] It is known that most roots of the nth derivatives of
is the Bessel function of the first kind of order