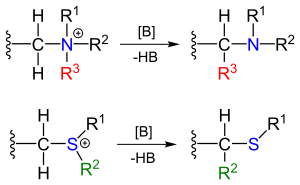
Stevens rearrangement
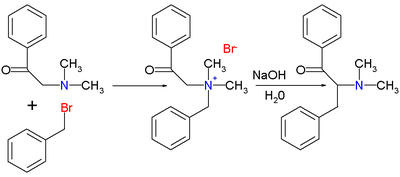
The original 1928 publication by Thomas S. Stevens[2] concerned the reaction of 1-phenyl-2-(N,N-dimethylamino)ethanone with benzyl bromide to the ammonium salt followed by the rearrangement reaction with sodium hydroxide in water to the rearranged amine.
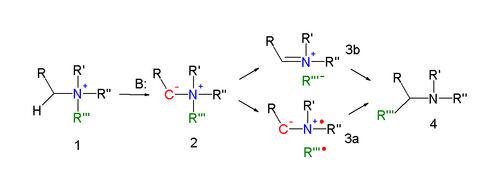
In an alternative reaction mechanism the N–C bond of the leaving group is homolytically cleaved to form a di-radical pair (3a).
In order to explain the observed retention of configuration, the presence of a solvent cage is invoked.
[7] The ylide is prepared in situ by reaction of the diazo compound ethyl diazomalonate with a sulfide catalyzed by dirhodium tetraacetate in refluxing xylene.
Recently, γ-butyrobetaine hydroxylase,[8][9] an enzyme that is involved in the human carnitine biosynthesis pathway, was found to catalyze a C-C bond formation reaction in a fashion analogous to a Stevens type rearrangement.