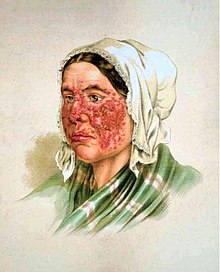
Lupus
[8] Females tend to have a greater number of relapses, a low white blood cell count, more arthritis, Raynaud syndrome, and psychiatric symptoms.
Males tend to have more seizures, kidney disease, serositis (inflammation of tissues lining the lungs and heart), skin problems, and peripheral neuropathy.
Because of early recognition and management of SLE with immunosuppressive drugs or corticosteroids,[35] end-stage renal failure occurs in less than 5%[36][37] of cases; except in the black population, where the risk is many times higher.
[38] This finding is due to immune complex deposition along the glomerular basement membrane, leading to a typical granular appearance in immunofluorescence testing.
[39] The diagnosis of neuropsychiatric syndromes concurrent with SLE (now termed as NPSLE),[40] is one of the most difficult challenges in medicine, because it can involve so many different patterns of symptoms, some of which may be mistaken for signs of infectious disease or stroke.
Cyclophosphamide (also known as Cytoxan), can lead to infertility by causing premature ovarian insufficiency (POI), the loss of normal function of one's ovaries prior to age forty.
[54] Methotrexate can cause termination or deformity in fetuses and is a common abortifacient, and for men taking a high dose and planning to father, a discontinuation period of 6 months is recommended before insemination.
cSLE typically is more severe and potentially lethal than adult-onset SLE because it often involves SLE-induced neurologic disease, renal failure, and/or the macrophage activation syndrome.
T cells, which regulate B-cell responses and infiltrate target tissues, have defects in signaling, adhesion, co-stimulation, gene transcription, and alternative splicing.
[87] Tingible body macrophages (TBMs) – large phagocytic cells in the germinal centers of secondary lymph nodes – express CD68 protein.
[88] Necrosis, a pro-inflammatory form of cell death, is increased in T lymphocytes, due to mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and depletion of ATP.
Most of the monocytes and tingible body macrophages (TBMs), which are found in the germinal centres of lymph nodes, even show a definitely different morphology; they are smaller or scarce and die earlier.
Close to TBM, follicular dendritic cells (FDC) are localised in GC, which attach antigen material to their surface and, in contrast to bone marrow-derived DC, neither take it up nor present it via MHC molecules.
The similarity and cross-reactivity between the initial targets of nRNP and Sm autoantibodies identifies a likely commonality in cause and a focal point for intermolecular epitope spreading.
[98] Elevated expression of HMGB1 was found in the sera of people and mice with systemic lupus erythematosus, high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) is a nuclear protein participating in chromatin architecture and transcriptional regulation.
A multianalyte panel (MAP) of autoantibodies, including ANA, anti-dsDNA, and anti-Smith in combination with the measurement of cell-bound complement activation products (CB-CAPs) with an integrated algorithm has demonstrated 80% diagnostic sensitivity and 86% specificity in differentiating diagnosed SLE from other autoimmune connective tissue diseases.
[13] Other ANA that may occur in people with SLE are anti-U1 RNP (which also appears in systemic sclerosis and mixed connective tissue disease), SS-A (or anti-Ro) and SS-B (or anti-La; both of which are more common in Sjögren's syndrome).
[107] The American College of Rheumatology (ACR) established eleven criteria in 1982,[108] which were revised in 1997[109] as a classificatory instrument to operationalise the definition of SLE in clinical trials.
Mycophenolic acid is also used for the treatment of lupus nephritis, but it is not FDA-approved for this indication, and FDA is investigating reports that it may be associated with birth defects when used by pregnant women.
[126][127] In more severe cases, medications that modulate the immune system (primarily corticosteroids and immunosuppressants) are used to control the disease and prevent recurrence of symptoms (known as flares).
Depending on the dosage, people who require steroids may develop Cushing's syndrome, symptoms of which may include obesity, puffy round face, diabetes mellitus, increased appetite, difficulty sleeping, and osteoporosis.
Women pregnant and known to have anti-Ro (SSA) or anti-La antibodies (SSB) often have echocardiograms during the 16th and 30th weeks of pregnancy to monitor the health of the heart and surrounding vasculature.
The mortality risk is fivefold when compared to the normal population in the late stages, which can be attributed to cardiovascular disease from accelerated atherosclerosis, the leading cause of death for people with SLE.
Studies have shown that self-reported data is affected by more than just the patient's experience with the disease- social support, the level of helplessness, and abnormal illness-related behaviors also factor into a self-assessment.
Additionally, other factors like the degree of social support that a person receives, socioeconomic status, health insurance, and access to care can contribute to an individual's disease progression.
[150] Research has also implicated XIST, which encodes a long non-coding RNA that coats the inactive member of the pair of X chromosomes in females as part of a ribonucleoprotein complex, as a source of autoimmunity.
[163] The 19th century's research into lupus continued with the work of Sir William Osler who, in 1895, published the first of his three papers about the internal complications of erythema exudativum multiforme.
Further study of the disease led to a third paper, published in 1903, documenting afflictions such as arthritis, pneumonia, the inability to form coherent ideas, delirium, and central nervous system damage as all affecting patients diagnosed with SLE.
[169] To ensure that the person has lupus and not another autoimmune disease, the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) established a list of clinical and immunologic criteria that, in any combination, point to SLE.
[173] In September 2022, researchers at the University of Erlangen-Nuremberg published promising results using genetically altered immune cells to treat severely ill patients.