Tabtoxin
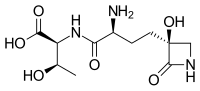
[1] It is produced by: Tabtoxin is a dipeptide precursor to the biologically active form of TBL, differing by having an extra threonine attached by a peptide bond to the C terminus.
Tabtoxin resistance protein (TTR) is an enzyme that catalyzes the acetylation of TBL, rendering tabtoxin-producing pathogens tolerant to their own phytotoxins.
The structure of an inactivated mutant of TTR is solved with its natural cofactor acetyl-CoA to 1.55 Å resolution.
The binary complex forms a characteristic “V” shape for substrate binding and contains the four motifs conserved in the GCN5-related N-acetyltransferase (GNAT) superfamily, which also includes the histone acetyltransferases (HATs).
A biosynthetic model for the formation of TβL resembles that of lysine, where the first dedicated step is the DapA-catalyzed condensation of aspartic acid semialdehyde with pyruvate to form L-2,3-dihydropicolinate (DHDPA).
tabaci, were examined by varying the components of a defined basal medium, which contained the following nutrients per liter: sucrose (10 g), KNO3 (5 g), MgSO4.7H2O (0.2 g), CaCl2.2H2O (0.11 g), FeSO4.7H2O (20 mg), NaH2PO4.2H2O (0.9 g) and H2PO4.3H2O[clarification needed] (1 g).