Target market
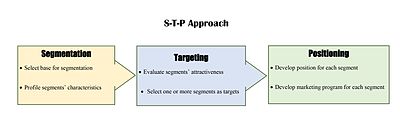
This allows the business to tailor its marketing activities with the needs, wants, aspirations and expectations of target customers in mind.
Also, targeting makes it possible to collect more precise data about customer needs and behaviors and then analyze that information over time in order to refine market strategies effectively.
For example, the potential market or TAM for feminine sanitary products might be defined as all women aged 14–50 years.
A profile will include all such information as is relevant for the product or service and may include basic demographic descriptors, purchasing habits, disposition to spend, benefits-sought, brand preferences, loyalty behavior, usage frequency and any other information deemed relevant to the subject at hand.
In the event that customer needs across the entire market are relatively similar, then the business may decide to use an undifferentiated approach.
An established stream of literature focussing on International Market Segmentation (IMS) suggests that international segmentation and targeting decisions employ a two-stage process:[15] Analysis carried out in the first stage focuses involves the collection of comparative information about different countries with a view to identifying the most valuable markets to enter.
During the research and analysis carried out during the segmentation and targeting process, the marketer will have gained insights into what motivates consumers to purchase a product or brand.
Firms typically develop a detailed positioning statement which includes the target market definition, the market need, the product name and category, the key benefit delivered and the basis of the product's differentiation from any competing alternatives.
[19] When implemented successfully, these activities should deliver a firm's products or services to target consumers in a cost efficient manner.
Instead, they relied on checklists or lengthy classifications of factors that needed to be considered to understand consumer responses.
The commonly accepted 7Ps of services marketing include: the original four Ps of product, price, place, promotion plus participants (people), physical evidence and process.
For maximum efficiency, distribution channels must identify where the target market are most likely to make purchases or access the product.
For instance, businesses may need to provide ramps for wheelchair access or baby change rooms for mothers.
Promotion refers to "the marketing communication used to make the offer known to potential customers and persuade them to investigate it further".
Research has generally shown that target marketing strategies are constructed from consumer inferences of similarities between some aspects of the advertisement (e.g., source pictured, language used, lifestyle represented) and characteristics of the consumer (e.g. reality or desire of having the represented style).
However, there are also negative aspects to mass marketing as not everyone thinks the same so it would be extremely difficult to get the same message across to a huge number of people (Ramya & Subasakthi).
But investing all the time, money and resources into differentiated marketing can be worth it if done correctly, as the different messages can successfully reach the targeted group of people and successfully motivate the targeted group of people to follow the messages that are being advertised (Ramya & Subasakthi).
This allows companies to have a competitive advantage over other larger firms targeting the same group; as a result, it generates higher profit margins.
Niche marketing is not only used for remaining at a competitive advantage in the industry but is also used as a way to attract more consumers and enlarge their client database.
Smaller firms can focus on finding out their clients problems within their niche and can then provide different marketing to appeal to consumer interest.
Firms use direct marketing a communication channel to interact and reach out to their existing consumers (Asllani & Halstead, 2015).
An important tool that organisations use in direct marketing is the RFM model (recency-frequency-monetary value) (Asllani & Halstead, 2015).
Data is captured from electronic communications devices, mapped and logged with a management information system.
This enables the integration of observed behaviour (domains accessed) with motives (content involvement), geographics (IP addresses), demographics (self-reported registration details) and brand preferences (site-loyalty, site stickiness).
[36] Marketers and advertisers can then use an inventory of stock images and phrases to compile customised promotion offers in real-time which are delivered to prospective purchasers with a strong interest in the product, or who are in an advanced state of buyer-readiness.
[37] With increased availability of electronic scanner data there has been a greater focus on research of micromarketing and pricing problems that retailers encounter.
In 1997, Alan Montgomery used hierarchical Bayes models to improve the estimation procedures of price elasticities, showing that micromarketing strategies can increase gross profits.
[38] With the advent of social media, advertising has become a more efficient at reaching relatively small target audiences.
The data they collect includes information such as the internet user's age, gender, race, and many other contributing factors.
[37] Those who are opposed of targeting in online advertising are still doubtful of its productivity, often arguing the lack of privacy given to internet users.