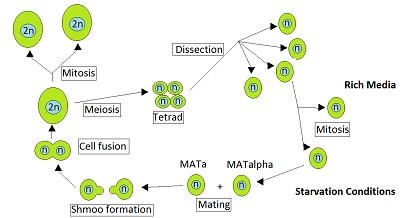
Tetrad (meiosis)
The tetrad is the four spores produced after meiosis of a yeast or other Ascomycota, Chlamydomonas or other alga, or a plant.
The meiotic products, spores, remain packaged in the parental cell body to produce the tetrad.
Non-parental ditype (NPD) is a spore that contains only the two recombinant-type ascospores (assuming two segregating loci).
Tetrad analysis can be used to confirm whether a phenotype is caused by a specific mutation, construction of strains, and for investigating gene interaction.
Tetrad analyses have also contributed to detection and study of the phenomena of gene conversion and post-meiotic segregation.