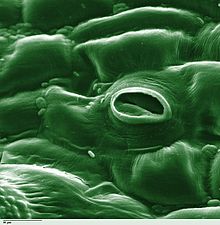
Transpiration
Transpiration is the process of water movement through a plant and its evaporation from aerial parts, such as leaves, stems and flowers.
[1] Transpiration also cools plants, changes osmotic pressure of cells, and enables mass flow of mineral nutrients.
Both of these factors influence the rate of bulk flow of water moving from the roots to the stomatal pores in the leaves via the xylem.
Capillary action is the process of a liquid flowing in narrow spaces without the assistance of, or even in opposition to, external forces like gravity.
The rate of transpiration is also influenced by the evaporative demand of the atmosphere surrounding the leaf such as boundary layer conductance, humidity, temperature, wind, and incident sunlight.
Factors that effect root absorption of water include: moisture content of the soil, excessive soil fertility or salt content, poorly developed root systems, and those impacted by pathogenic bacteria and fungi such as pythium or rhizoctonia.
[10] Transpiration rates of plants can be measured by a number of techniques, including potometers, lysimeters, porometers, photosynthesis systems and thermometric sap flow sensors.
Many cacti conduct photosynthesis in succulent stems, rather than leaves, so the surface area of the shoot is very low.
This then allows for the roots to generate over 0.05 mPa of pressure, and that is capable of destroying the blockage and refilling the xylem with water, reconnecting the vascular system.
[18] Scientists have begun using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to monitor the internal status of the xylem during transpiration, in a non invasive manner.
These observations suggest that MRIs are capable of monitoring the functional status of xylem and allows scientists to view cavitation events for the first time.
Excess heat generated from solar radiation is damaging to plant cells and thermal injury occurs during drought or when there is rapid transpiration which produces wilting.
[19] Green vegetation contributes to moderating climate by being cooler than adjacent bare earth or constructed areas.
As plant leaves transpire they use energy to evaporate water aggregating up to a huge volume globally every day.
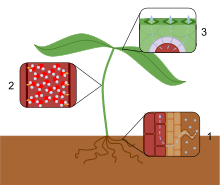
- Water is passively transported into the roots and then into the xylem .
- The forces of cohesion and adhesion cause the water molecules to form a column in the xylem.
- Water moves from the xylem into the mesophyll cells, evaporates from their surfaces and leaves the plant by diffusion through the stomata