Triangulation (surveying)
Such triangulation methods were used for accurate large-scale land surveying until the rise of global navigation satellite systems in the 1980s.
Triangulation today is used for many purposes, including surveying, navigation, metrology, astrometry, binocular vision, model rocketry and gun direction of weapons.
In the field, triangulation methods were apparently not used by the Roman specialist land surveyors, the agrimensores; but were introduced into medieval Spain through Arabic treatises on the astrolabe, such as that by Ibn al-Saffar (d.
[1] Abu Rayhan Biruni (d. 1048) also introduced triangulation techniques to measure the size of the Earth and the distances between various places.
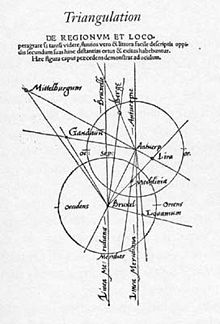
On land, the cartographer Gemma Frisius proposed using triangulation to accurately position far-away places for map-making in his 1533 pamphlet Libellus de Locorum describendorum ratione (Booklet concerning a way of describing places), which he bound in as an appendix in a new edition of Peter Apian's best-selling 1524 Cosmographica.
[3] In England Frisius's method was included in the growing number of books on surveying which appeared from the middle of the century onwards, including William Cuningham's Cosmographical Glasse (1559), Valentine Leigh's Treatise of Measuring All Kinds of Lands (1562), William Bourne's Rules of Navigation (1571), Thomas Digges's Geometrical Practise named Pantometria (1571), and John Norden's Surveyor's Dialogue (1607).
[4] The modern systematic use of triangulation networks stems from the work of the Dutch mathematician Willebrord Snell, who in 1615 surveyed the distance from Alkmaar to Breda, approximately 72 miles (116 kilometres), using a chain of quadrangles containing 33 triangles in all.
Meanwhile, the mathematician Carl Friedrich Gauss was entrusted from 1821 to 1825 with the triangulation of the kingdom of Hanover (Gaussian land survey [de]), on which he applied the method of least squares to find the best fit solution for problems of large systems of simultaneous equations given more real-world measurements than unknowns.