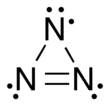
Trinitrogen
Triazirene (cyclic) Trinitrogen also known as the azide radical is an unstable molecule composed of three nitrogen atoms.
[5] As a linear and symmetric molecule, it has D∞h symmetry, with a nitrogen–nitrogen bond length averaging 1.8115 Å.
[1] The cyclic form was identified in 2003 by N. Hansen and A. M. Wodtke using ultraviolet photolysis of chlorine azide.
Although the reaction yielded mostly the linear form, about 20% of the molecules were cyclic.
[4][1] The ring has C2v symmetry[1]—an isosceles triangle—in contrast to the linear form that has equal N–N bond-lengths.