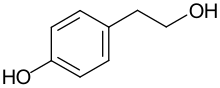
Tyrosol
Classified as a phenylethanoid, a derivative of phenethyl alcohol, it is found in a variety of natural sources.
[1][2] As an antioxidant, tyrosol may protect cells against injury due to oxidation in vitro.
[3] Although it is not as potent as other antioxidants present in olive oil (e.g., hydroxytyrosol), its higher concentration and good bioavailability indicate that it may have an important overall effect.
Tyrosol-treated animals showed significant increase in the phosphorylation of Akt, eNOS, and FOXO3a.
[6] Tyrosol forms esters with a variety of organic acids.