Economic history of the United States
According to a 2023 study, the plains were dominated by "organized, complex agricultural communities with settled populations that had opened and cleared land, domesticated plants, crafted irrigation systems, and determined the best rotation and fallow practices for a given region.
North Carolina was the leading producer of naval stores, which included turpentine (used for lamps), rosin (candles and soap), tar (rope and wood preservative) and pitch (ships' hulls).
He argues they grew from small villages to take major leadership roles in promoting trade, land speculation, immigration, and prosperity, and in disseminating the ideas of the Enlightenment, and new methods in medicine and technology.
At that time, half of the wrought iron, beaver hats, cordage, nails, linen, silk, and printed cotton produced in Britain were consumed by the British American colonies.
Many of the great American economists of the time, until the last quarter of the 19th century, were strong advocates of industrial protection: Daniel Raymond who influenced Friedrich List, Mathew Carey and his son Henry, who was one of Lincoln's economic advisers.
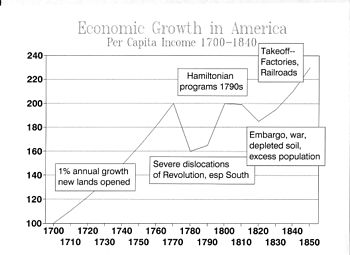
[45] In this report, Hamilton also proposed export bans on major raw materials, tariff reductions on industrial inputs, pricing and patenting of inventions, regulation of product standards and development of financial and transportation infrastructure.
Hamilton successfully argued for the concept of "implied powers", whereby the federal government was authorized by the Constitution to create anything necessary to support its contents, even if it not specifically noted in it (build lighthouses, etc.).
[65] Specific government programs and policies which gave shape and form to the American School and the American System include the establishment of the Patent Office in 1802; the creation of the Coast and Geodetic Survey in 1807 and other measures to improve river and harbor navigation; the various Army expeditions to the west, beginning with the Lewis and Clark Expedition in 1804 and continuing into the 1870s, almost always under the direction of an officer from the United States Army Corps of Topographical Engineers, and which provided crucial information for the overland pioneers that followed; the assignment of Army Engineer officers to assist or direct the surveying and construction of the early railroads and canals; the establishment of the First Bank of the United States and Second Bank of the United States as well as various protectionist measures (e.g., the tariff of 1828).
The Whig Party supported Clay's American System, which proposed to build internal improvements (e.g. roads, canals and harbors), protect industry, and create a strong national bank.
[68] New Orleans and St. Louis joined the United States and grew rapidly; entirely new cities were begun at Pittsburgh, Marietta, Cincinnati, Louisville, Lexington, Nashville and points west.
[9]: 133 To facilitate westward expansion, in 1801 Thomas Jefferson began work on the Natchez Trace, which was to connect Daniel Boone's Wilderness Road, which ended in Nashville, Tennessee, with the Mississippi River.
[9]: 88–100 A combination of domestic and foreign investment along with the discovery of gold and a major commitment of America's public and private wealth, enabled the nation to develop a large-scale railroad system, establishing the base for the country's industrialization.
[80] Historian Larry Haeg argues from the perspective of the end of the 19th century: The most important technological innovation in mid-19th-century pig iron production was the adoption of hot blast, which was developed and patented in Scotland in 1828.
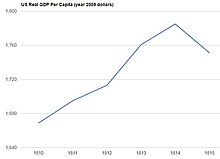
The panic was triggered by the August 24 failure of the well regarded Ohio Life Insurance and Trust Co. A manager in the New York branch, one of the city's largest financial institutions, had embezzled funds and made excessive loans.
Secretary Chase, though a long-time free-trader, worked with Congressman Justin Morrill to pass a second tariff bill in summer 1861, raising rates another 10 points in order to generate more revenues.
In addition to operating revenues, railroads were able to finance networks crossing vast distances by selling granted property adjacent to the tracks; these would become highly desirable plots for new settlers and businesses because of the easy access to long-distance transportation.
British Parliamentary Committee members Joseph Whitworth and George Wallis were very impressed at the educational level of workers in the U.S., commenting that "so that everybody reads ... and intelligence penetrates through the lowest grades of society."
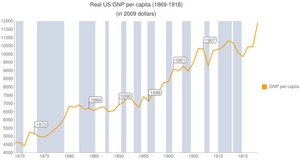
Improvements in transportation and other technological progress caused prices to fall, especially during the so-called long depression, but the rising amount of gold and silver being mined eventually resulted in mild inflation during the 1890s and beyond.
John D. Rockefeller was the master planner and organizer of the systematic plan to form combinations with or acquire competitors and enter all phases of the oil industry from production to transportation, refining and distribution, a concept called vertical integration.
Efficient gas mantles and electric lighting were eroding the illuminating oil market beginning in the 1880s; however a previously low value byproduct of refining was gasoline, which more than offset the role of kerosene in the early 20th century.
Spending would go up and America would get out of the great depression when World War II happened after Japan's attack on American forces in Pearl Harbor in December 1941 led to much sharper increases in government purchases, and the economy pushed quickly into an inflationary gap.
The federal programs launched by Hoover and greatly expanded by president Roosevelt's New Deal used massive construction projects to try to jump start the economy and solve the unemployment crisis.
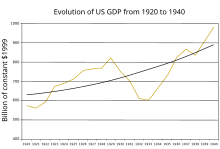
If one defines economic health entirely by the gross domestic product, the U.S. had gotten back on track by 1934, and made a full recovery by 1936, but as Roosevelt said, one third of the nation was ill fed, ill-housed and ill-clothed.
The "Baby Boom" saw a dramatic increase in fertility in the period 1942–1957; it was caused by delayed marriages and childbearing during depression years, a surge in prosperity, a demand for suburban single-family homes (as opposed to inner city apartments) and new optimism about the future.
Developers purchased empty land just outside the city, installed tract houses based on a handful of designs, and provided streets and utilities, or local public officials race to build schools.
[252][253] Union membership has continued to decline into the 2010s due to right-to-work laws adopted by many states, globalization undermining higher-wage firms, and increasing political opposition exemplified by the breaking of the 1981 strike of the Professional Air Traffic Controllers Organization (1968) by President Ronald Reagan.
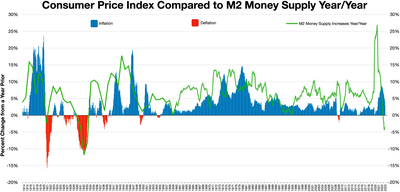
Interest rates remained high, with the prime reaching 20% in January 1981; Art Buchwald quipped that 1980 would go down in history as the year when it was cheaper to borrow money from the Mafia than the local bank.
But at the same time, most orthodox economists, and most policy makers, pointed to the fact that consumers could buy so many goods, even with the inflation of the 1970s, as evidence that the general shift away from manufacturing and into services was creating widespread prosperity.
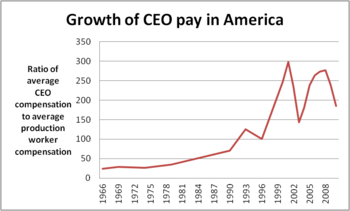
Critics however argued that this consumer behavior was giving a false reading of the health of the economy, because it was being paid for by taking on rapidly increasing levels of indebtedness, thus covering up the stagnating wages and earnings of most of the workforce.
[295] Five months after the decision was made, the American stock markets suffered their biggest crash in modern U.S. history as a result of concerns surrounding the coronavirus pandemic and the Russia-Saudi Arabia oil price war.