(Bis(trifluoroacetoxy)iodo)benzene
(Bis(trifluoroacetoxy)iodo)benzene, C6H5I(OCOCF3)2, is a hypervalent iodine compound used as a reagent in organic chemistry.
[1] The syntheses of all aryl hypervalent iodine compounds start from iodobenzene.
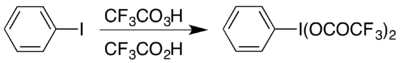
The compound can be prepared by reaction of iodobenzene with a mixture of trifluoroperacetic acid and trifluoroacetic acid in a method analogous to the synthesis of (diacetoxyiodo)benzene:[1] It can also be prepared by dissolving diacetoxyiodobenzene (a commercially-available compound) with heating in trifluoroacetic acid:[2] It also brings around the conversion of a hydrazone to a diazo compound, for example in the diazo-thioketone coupling.
The Hofmann rearrangement is a decarbonylation reaction whereby an amide is converted to an amine by way of an isocyanate intermediate.
[3][4] The reaction can also be carried out under mildly acidic conditions by way of the same intermediate using a hypervalent iodine compound in aqueous solution.