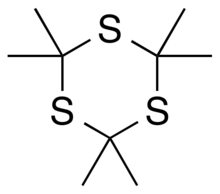
Trithioacetone
[4][2] It can be viewed as a derivative of 1,3,5-trithiane, with methyl-group substituents for all of the hydrogen atoms in that parent structure.
Trithioacetone was first made in 1889 by Baumann and Fromm, by reaction of hydrogen sulfide with acetone.
[6] In the presence of an acidified ZnCl2 catalyst at 25 °C, one obtains a product that is 60–70% trithioacetone, 30–40% of 2,2-propanedithiol, and small amounts of two isomeric impurities, 3,3,5,5,6,6-hexamethyl-1,2,4-trithiane and 4-mercapto-2,2,4,6,6-pentamethyl-1,3-dithiane.
[6] The product can also be obtained by pyrolysis of allyl isopropyl sulfide.
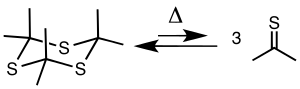
[7][8] Pyrolysis of trithioacetone at 500–650 °C and 5–20 mm of Hg gives thioacetone, that can be collected by a cold trap at −78 °C.