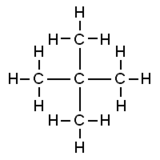
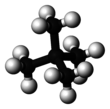
Neopentane
[8][9] The boiling point of neopentane is only 9.5 °C, significantly lower than those of isopentane (27.7 °C) and normal pentane (36.0 °C).
Therefore, neopentane is a gas at room temperature and atmospheric pressure, while the other two isomers are (barely) liquids.
This anomaly has been attributed to the better solid-state packing assumed to be possible with the tetrahedral neopentane molecule; but this explanation has been challenged on account of it having a lower density than the other two isomers.
[11] In this respect, neopentane is similar to its silane analog, tetramethylsilane, whose single chemical shift is zero by convention.
In particular, if each methyl group has a different number of substituted atoms (0, 1, 2, and 3), one obtains a chiral molecule.