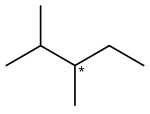
2,3-Dimethylpentane
It is an alkane ("paraffin" in older nomenclature), a fully saturated hydrocarbon; specifically, one of the isomers of heptane.
Like typical alkanes, it is a colorless flammable compound; under common ambient conditions, it is a mobile liquid, less dense than water.
Most properties listed in the literature refer to the racemic compound (an equimolar mixture of the two enantiomers).
[7][8][9] The racemic mixture has a glass transition temperature of about 123 K (−150 °C), but reportedly it does not crystallize—a fact that has been claimed to be a characteristic of high-purity optically active alkanes.
[4][6][10] 2,3-Dimethylpentane is practically absent in the synthetic fuel produced from hydrogen and carbon monoxide by the Fischer–Tropsch process.