Carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a poisonous, flammable gas that is colorless, odorless, tasteless, and slightly less dense than air.
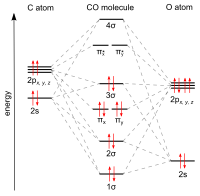
Carbon monoxide is the simplest oxocarbon and is isoelectronic with other triply bonded diatomic species possessing 10 valence electrons, including the cyanide anion, the nitrosonium cation, boron monofluoride and molecular nitrogen.
If carbon monoxide acts as a ligand, the polarity of the dipole may reverse with a net negative charge on the oxygen end, depending on the structure of the coordination complex.
[27] Typical concentrations in parts per million are as follows: Carbon monoxide (CO) is present in small amounts (about 80 ppb) in the Earth's atmosphere.
[36] Small amounts are also emitted from the ocean, and from geological activity because carbon monoxide occurs dissolved in molten volcanic rock at high pressures in the Earth's mantle.
Carbon monoxide has an indirect effect on radiative forcing by elevating concentrations of direct greenhouse gases, including methane and tropospheric ozone.
If the hydrogen partial pressure is high enough (for instance in an underground sea), formic acid will be formed: These reactions can take place in a few million years even at temperatures such as found on Pluto.
[48] Carbon monoxide is a temporary atmospheric pollutant in some urban areas, chiefly from the exhaust of internal combustion engines (including vehicles, portable and back-up generators, lawnmowers, power washers, etc.
), but also from incomplete combustion of various other fuels (including wood, coal, charcoal, oil, paraffin, propane, natural gas, and trash).
Carbon monoxide may be emitted from tobacco smoke and generated from malfunctioning fuel burning stoves (wood, kerosene, natural gas, propane) and fuel burning heating systems (wood, oil, natural gas) and from blocked flues connected to these appliances.
[8] In developed countries the main sources of indoor CO emission come from cooking and heating devices that burn fossil fuels and are faulty, incorrectly installed or poorly maintained.
Chronic exposure to low concentrations of carbon monoxide may lead to lethargy, headaches, nausea, flu-like symptoms and neuropsychological and cardiovascular issues.
Some metal–CO complexes are prepared by decarbonylation of organic solvents, not from CO. For instance, iridium trichloride and triphenylphosphine react in boiling 2-methoxyethanol or DMF to afford IrCl(CO)(PPh3)2.
[60] The compounds cyclohexanehexone or triquinoyl (C6O6) and cyclopentanepentone or leuconic acid (C5O5), which so far have been obtained only in trace amounts, can be regarded as polymers of carbon monoxide.
[72] Landis also proposed manufacturing the fuel from the similar carbon dioxide atmosphere of Venus for a sample return mission, in combination with solar-powered UAVs and rocket balloon ascent.
Because of carbon monoxide's role in the body, abnormalities in its metabolism have been linked to a variety of diseases, including neurodegenerations, hypertension, heart failure, and pathological inflammation.
[77] In animal model studies, carbon monoxide reduced the severity of experimentally induced bacterial sepsis, pancreatitis, hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury, colitis, osteoarthritis, lung injury, lung transplantation rejection, and neuropathic pain while promoting skin wound healing.
Therefore, there is significant interest in the therapeutic potential of carbon monoxide becoming pharmaceutical agent and clinical standard of care.
The benefit is two-fold, carbon monoxide protects against microbial spoilage and it enhances the meat color for consumer appeal.
[87] The technology was first given "generally recognized as safe" (GRAS) status by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2002 for use as a secondary packaging system, and does not require labeling.
[54] Carbon monoxide had been used for genocide during the Holocaust at some extermination camps, the most notable by gas vans in Chełmno, and in the Action T4 "euthanasia" program.
The early development of metallurgy and smelting technologies emerging circa 6,000 BC through the Bronze Age likewise plagued humankind from carbon monoxide exposure.
Greek physician Galen (129–199 AD) speculated that there was a change in the composition of the air that caused harm when inhaled, and many others of the era developed a basis of knowledge about carbon monoxide in the context of coal fume toxicity.
[54] Georg Ernst Stahl mentioned carbonarii halitus in 1697 in reference to toxic vapors thought to be carbon monoxide.
Herman Boerhaave conducted the first scientific experiments on the effect of carbon monoxide (coal fumes) on animals in the 1730s.
Later in 1776, the French chemist de Lassone [fr] produced CO by heating zinc oxide with coke, but mistakenly concluded that the gaseous product was hydrogen, as it burned with a blue flame.
[54][93] Thomas Beddoes and James Watt recognized carbon monoxide (as hydrocarbonate) to brighten venous blood in 1793.
[54] The mechanism for carbon monoxide poisoning is widely credited to Claude Bernard whose memoirs beginning in 1846 and published in 1857 phrased, "prevents arterials blood from becoming venous".
Originally developed as part of the German war effort to compensate for their lack of domestic petroleum, this technology continues today.
This process, called hydroformylation, is used to produce many large scale chemicals such as surfactants as well as specialty compounds that are popular fragrances and drugs.