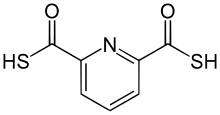
2,6-Pyridinedicarbothioic acid
[1] PDTC can be synthesized in the laboratory by treating the diacid dichloride of pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylic with H2S in pyridine: This route produces the pyridinium salt of pyridinium-2,6-dicarbothioate.
Treatment of this orange-colored salt with sulfuric acid gives colorless PDTC, which can then be extracted with dichloromethane.
[2] The biosynthesis of PDTC remains unclear although some insights can be deduced from the genetics.
[3] It is suggested that Pseudomonas stutzeri may have acquired at least one of the genes by lateral transfer from mycobacteria.
[4] In a proposed biosynthetic sequence pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylic acid, a known bacterial metabolite,[4] is activated as its bis-adenosine monophosphate (AMP) derivative.