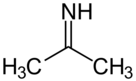
Acetone imine
It is a volatile and flammable liquid at room temperature.
Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (CyN=C=NCy) serves as the scavenger for hydrogen cyanide:[2] The compound hydrolyzes readily: This reactivity is characteristic of imines derived from ammonia.
Methylene imine (CH2=NH) is also highly reactive, condensing to hexamethylenetetramine.
Upon standing, acetone imine undergoes further condensation to give the tetrahydropyrimidine called acetonin, with loss of ammonia.
[3] The imine of hexafluoroacetone, ((CF3)2C=NH) is by contrast robust.