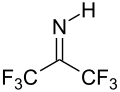
Hexafluoroacetone
It is a colourless, hygroscopic, nonflammable, highly reactive gas characterized by a musty odour.
[2] According to electron diffraction, HFA and acetone adopt very similar structures, the C-O distance being only longer in the fluorinated compound (124.6 vs 121.0 pm), possibly due to steric effects.
[5] It has also be prepared from hexafluoropropylene oxide, which will rearrange to give HFA when heated in the presence of a Lewis acid such as AlCl3.
[7] In the first step KF catalyzes the reaction of the alkene with elemental sulfur to give the 1,3-dithietane dimer of hexafluorothioacetone.
[8] Hexafluoroacetone is used in the production of hexafluoroisopropanol: It is also used as a precursor to hexafluoroisobutylene,[4] a monomer used in polymer chemistry, and as a building block in the synthesis of midaflur, bisphenol AF, 4,4′-(hexafluoroisopropylidene)diphthalic anhydride, and alitame.