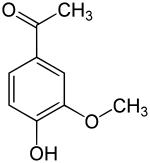
Apocynin
Apocynin's observed anti-inflammatory capabilities proved to be a result of its ability to selectively prevent the formation of free radicals, oxygen ions, and peroxides in the body.
[6][7] Apocynin was used to determine whether ionic activation due to proton flux across the membrane of renal medulla cells was coupled to NADPH oxidase production of superoxide.
Apocynin was introduced to the cells and completely blocked the production of superoxide, and was a key component in determining that the proton outflow was responsible for the activation of NADPH oxidase.
[9] Although, diapocynin seems to have beneficial effect in reducing reactive oxygen species and anti-inflammatory properties, it is still yet to be shown as biologically relevant molecule.
[11] Small scale early stage clinical trials for apocynin were conducted for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in 2011[12] and asthma in 2012[13] but they did not progress any further.