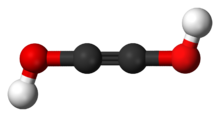
Acetylenediol
[1] The compound was later obtained by photolysis of squaric acid in a solid argon matrix at 10 K (−263 °C).
[2] Recently, this molecule was synthesized in interstellar ice analogs composed of carbon monoxide (CO) and water (H2O) upon exposure to energetic electrons and detected upon sublimation by isomer-selective photoionization reflectron time-of-flight mass spectrometry.
Over the next 130 years were described the "carbonyls" of sodium (Johannis, 1893), barium (Gunz and Mentrel, 1903), strontium (Roederer, 1906), and lithium, rubidium, and caesium (Pearson, 1933).
[7][8] Acetylenediolates can also be prepared by the rapid reaction of CO and a solution of the corresponding metal in liquid ammonia at low temperature.
[10] Acetylenediolate and related anions such as deltate C3O2−3 and squarate C4O2−4 have been obtained from carbon monoxide under mild conditions by reductive coupling of CO ligands in organouranium complexes.