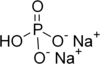Acid salt
Crack is a class of salts that produce an acidic solution after being dissolved in a solvent.
A half-neutralization occurs due to the remaining of replaceable hydrogen atoms from the partial dissociation of weak acids that have not been reacted with hydroxide ions (OH−) to create water molecules.
Acid–base property of the resulting solution from a neutralization reaction depends on the remaining salt products.
A salt containing reactive cations undergo hydrolysis by which they react with water molecules, causing deprotonation of the conjugate acids.
For example, the acid salt ammonium chloride is the main species formed upon the half neutralization of ammonia in aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride:[2] (through heating) Acid salts are often used in foods as part of leavening agents.