Airway pressure release ventilation
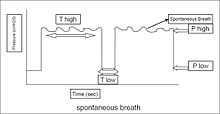
[5] Based on clinical and experimental data, airway pressure release ventilation is indicated in patients with acute lung injury,[6][7] acute respiratory distress syndrome[8][9] and atelectasis[1] after major surgery This is a type of inverse ratio ventilation.
Mean airway pressure on APRV is calculated by this formula:[1] Different perceptions of this mode may exist around the globe.
While 'APRV' is common to users in North America, a very similar mode, biphasic positive airway pressure (BIPAP), was introduced in Europe.
Although similar in modality, these terms describe how a mode is intended to inflate the lung, rather than defining the characteristics of synchronization or the way spontaneous breathing efforts are supported.
[8][15] Concern has been raised about the amount of mechanical power applied to the lung during APRV and the risk of ergotrauma, especially in pulmonary ARDS.