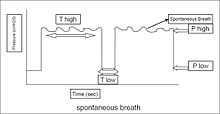
Mean airway pressure
Mean airway pressure correlates with alveolar ventilation, arterial oxygenation,[1] hemodynamic performance, and barotrauma.
[2] It can also match the alveolar pressure if there is no difference between inspiratory and expiratory resistance.
[3] There are several equations aimed at determining the real mean airway pressure.
[6] MAP is closely associated with mean alveolar pressure and shows the stresses exerted on the lung parenchyma on mechanical ventilation.
[7] In high frequency oscillatory ventilation, it has been suggested to set the mean airway pressure six above the lower inflection point on the lungs P-V curve.