Alamethicin
Alamethicin is a channel-forming peptide antibiotic, produced by the fungus Trichoderma viride.
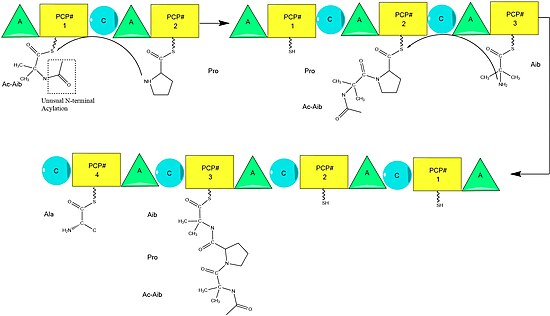
The peptide sequence is where Ac = acetyl, Phl = phenylalaninol, and Aib = 2-Aminoisobutyric acid.
In cell membranes, it forms voltage-dependent ion channels by aggregation of four to six molecules.
[2] Although there are several sequences of the alamethicin peptide accepted,[3] evidence suggests these all follow the general NRPS mechanism [4] with small variations at select amino acids.
[8] The growing chain is attached to the amino acid bearing PCP by the "condensation" (C) domain, followed by another round of the same reactions by the next module.