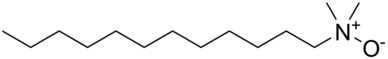
Amine oxide
It contains a nitrogen-oxygen coordinate covalent bond with three additional hydrogen and/or substituent-groups attached to nitrogen.
Amine oxides are surfactants commonly used in consumer products such as shampoos, conditioners, detergents, and hard surface cleaners.
[4] They serve as stabilizers, thickeners, emollients, emulsifiers, and conditioners with active concentrations in the range of 0.1–10%.
[2] The remainder (< 5%) is used in personal care, institutional, commercial products[5] and for unique patented uses such as photography.
Chronic ingestion by rabbits found lower body weight, diarrhea, and lenticular opacities at a lowest observed adverse effect levels (LOAEL) in the range of 87–150 mg AO/kw bw/day.
Eye irritation due to amine oxides and other surfactants is moderate and temporary with no lasting effects.
They are considered to have low bioaccumulation potential in aquatic species based on log Kow data from chain lengths less than C14 (bioconcentration factor < 87%).
The highest effluent concentrations were found in oxidation ditch and trickling filter treatment plants.