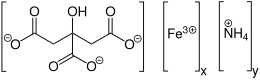
Ammonium ferric citrate
All three carboxyl groups and the central hydroxyl group of citric acid are deprotonated.
A distinguishing feature of this compound is that it is very soluble in water, in contrast to ferric citrate which is not very soluble.
[3] In its crystal structure each moiety of citric acid has lost four protons.
The deprotonated hydroxyl group and two of the carboxylate groups ligate to the ferric center, while the third carboxylate group coordinates with the ammonium.
[1] Ammonium ferric citrate has a range of uses, including: