Neighbouring group participation
In organic chemistry, neighbouring group participation (NGP, also known as anchimeric assistance) has been defined by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) as the interaction of a reaction centre with a lone pair of electrons in an atom or the electrons present in a sigma or pi bond contained within the parent molecule but not conjugated with the reaction centre.
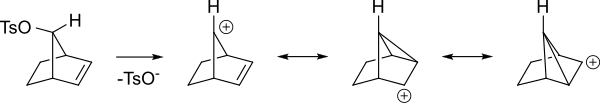
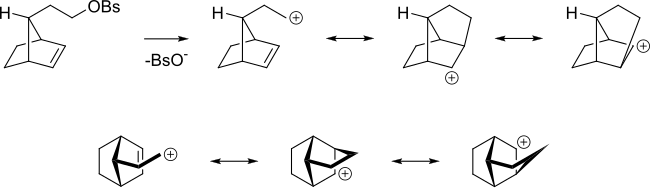
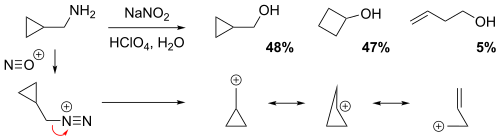
[5] The π orbitals of an alkene can stabilize a transition state by helping to delocalize the positive charge of the carbocation.
[6] In the non-classical perspective, the positive charge is delocalized throughout the carbocation intermediate structure via resonance, resulting in partial (electron-deficient) bonds.
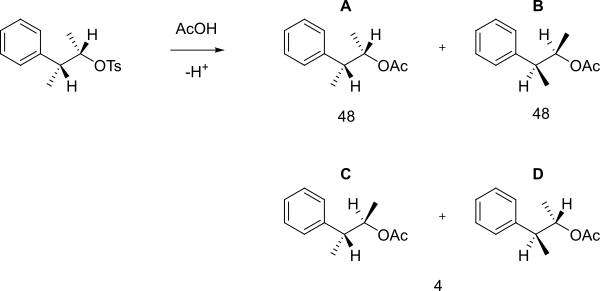
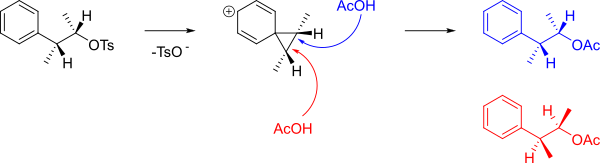
An aromatic ring can assist in the formation of a carbocationic intermediate called a phenonium ion by delocalising the positive charge.
When the following tosylate reacts with acetic acid in solvolysis then rather than a simple SN2 reaction forming B, a 48:48:4 mixture of A, B (which are enantiomers) and C+D was obtained.