Apoptosis regulator BAX
BCL2 family members form hetero- or homodimers and act as anti- or pro-apoptotic regulators that are involved in a wide variety of cellular activities.
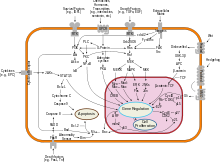
This protein is reported to interact with, and increase the opening of, the mitochondrial voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC), which leads to the loss in membrane potential and the release of cytochrome c. The expression of this gene is regulated by the tumor suppressor P53 and has been shown to be involved in P53-mediated apoptosis.
[16] Alternatively, growing evidence also suggests that activated BAX and/or Bak form an oligomeric pore, MAC in the MOM (mitochondrial outer membrane).
BAX activation is stimulated by various abiotic factors, including heat, hydrogen peroxide, low or high pH, and mitochondrial membrane remodeling.
The p53 protein is a transcription factor that, when activated as part of the cell's response to stress, regulates many downstream target genes, including BAX.
Wild-type p53 has been demonstrated to upregulate the transcription of a chimeric reporter plasmid utilizing the consensus promoter sequence of BAX approximately 50-fold over mutant p53.