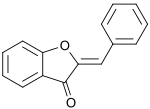
Aurone
An aurone is a heterocyclic chemical compound, which is a type of flavonoid.
The molecule contains a benzofuran element associated with a benzylidene linked in position 2.
[2] Aurones including 4'-chloro-2-hydroxyaurone (C15H11O3Cl) and 4'-chloroaurone (C15H9O2Cl) can also be found in the brown alga Spatoglossum variabile.
[3] Most aurones are in a (Z)-configuration, which is the more stable configuration according to Austin Model 1 computation.
[5] Aureusidin synthase catalyzes the creation of aurones from chalcones through hydroxylation and oxidative cyclization.