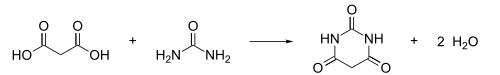
Barbituric acid
Barbituric acid or malonylurea or 6-hydroxyuracil is an organic compound based on a pyrimidine heterocyclic skeleton.
It remains unclear why Baeyer chose to name the compound that he discovered "barbituric acid".
[12] Barbituric acid is a chemical building block in the laboratory synthesis of riboflavin (vitamin B2) and in a method of producing the pharmaceutical drug minoxidil.
[14][15][16][17] Barbiturates are dependence-producing, and abrupt cessation of high doses can result in a very medically serious, even lethal, withdrawal syndrome.
Barbituric acid derivatives are considered DEA Schedule III controlled substances.