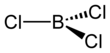
Boron trichloride
[4] BCl3 does not dimerize, although NMR studies of mixtures of boron trihalides shows the presence of mixed halides.
As a strong Lewis acid, BCl3 forms adducts with tertiary amines, phosphines, ethers, thioethers, and halide ions.
-93 °C) is a planar molecule in the solid, (similar to dinitrogen tetroxide, but in the gas phase the structure is staggered.
[4] It decomposes (disproportionates) at room temperatures to give a series of monochlorides having the general formula (BCl)n, in which n may be 8, 9, 10, or 11.
It is also used in the refining of aluminium, magnesium, zinc, and copper alloys to remove nitrides, carbides, and oxides from molten metal.
In the manufacture of electrical resistors, a uniform and lasting adhesive carbon film can be put over a ceramic base using BCl3.
It has been used in the field of high energy fuels and rocket propellants as a source of boron to raise BTU value.