Braak staging
In particular, this death occurs in the ventral part of the pars compacta, with up to 70% of the cells affected by the time the patient dies.
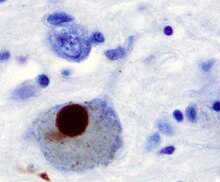
[3] One mechanism consists of an abnormal accumulation of the protein alpha-synuclein bound to ubiquitin in the damaged cells.
The presence of Lewy bodies in the enteric and peripheral nervous systems supports their claim.
This Lewy body pathology selectively travels through the CNS, targeting thin and largely unmyelinated neurons.
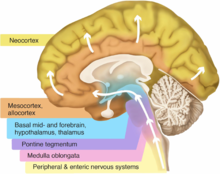
[6] Braak and colleagues further state that the disease begins in the enteric nervous system and gains entry to the CNS through the vagus nerve.
[4][6] The disease then moves up the brainstem, traveling from the medullary structures to the locus ceruleus in the pontine tegmentum.
[4][6] The disease has started to invade the neocortex and spreads into the structures of the temporal, parietal, and frontal lobes.

B. Localization of the area of significant brain volume reduction in initial PD compared with a group of participants without the disease in a neuroimaging study which concluded that brain stem damage may be the first identifiable stage of PD neuropathology . [ 1 ]