CREB-binding protein
[7][11][12] For example, CBP alone has been implicated in a wide variety of pathophysiologies including colorectal cancer as well as head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
[8] The CH2 region, located in the middle of the protein, in its acetyltransferase domain, does not contain this consensus sequence, and has not been conclusively shown to bind zinc ions.
[19] Interestingly, these helices can fold into a number of different conformers which enables the domain to maintain both a level of promiscuity while also exerting regulatory control.
[18] The 380 protein residue lysine acetyltransferase (KAT) domain is arguably one of the most important and identifying structural components of CBP.
CBP has two critical mechanisms by which it is able to regulate gene expression: as an acetyltransferase, and as a protein scaffold that helps recruit and construct the complexes that are necessary for transcription or chromatin remodeling.
Phosphorylation of CBP increases its acetyltransferase activity, a process hypothesized to be regulated in a cell cycle dependent manner.
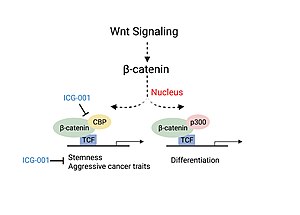
[18] In an experiment performed involving the Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus, the pathological protein (vIRF), was shown to be upregulated by CBP and repressed by p300.
[12] p300 homozygous knockout studies in mice were embryonic lethal, with improper neurulation and poor heart development occurring during their limited survival.
[18] The fact that both CBP and p300 homozygous knockouts were embryonic lethal suggest that these factors play a critical role in embryogenesis.
Studies performed in the late 1990s demonstrated that peak CBP acetyltransferase activity occurs at the transition between the G1/S phase of the cell cycle checkpoint.
CBP (and p300) have been shown to interact with E2F proteins as both a coactivator, and as an acetyltransferase, the latter of which causes increased E2F DNA binding affinity.
This complex consists of numerous subunits that are grouped into two subdomains, the "Arc Lamp" and the "Platform," and functions as an E3 ubiquitin ligase that targets components related to the cell cycle such as cyclin B, securin, and PLK1 for proteasome degradation.
[23] CBP and p300 play a role in the acetylation of DNA damage response proteins and this post-translational modification influences their function.
[12] Statistics indicate that RTS patients have and increased risk of cancer, with approximately 5% of that attributable to pediatric malignancies originating from the neural crest.
[8] Due to its critical role in regulation of cell proliferation, growth, migration and apoptosis, it is considered to be an oncogene, or tumor suppressor.
[18] In cases of patients diagnosed with Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) and Myelodysplastic Syndrome, CBP has been shown to gain function.
[12] For patients with a relapsing case of Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL), it was reported approximately 18% of them had CBP KAT domain mutations.
[11][13] Increased nuclear hormone signaling, mediated by the androgen (AR) and estrogen (ER) receptors, are responsible for a number of prostate and breast cancer cases, respectively.
Inhibition of CBP KAT activity has been shown to decrease AR and ER signaling by down regulating receptor expression; this in turn suppresses tumorigenesis of both malignancies.
Numerous animal models have been designed in order to evaluate changes in motor, learning and memory function in mice with CBP mutations.
[22] For mice with homozygous point mutations in their CBP KIX domain, they demonstrated impaired motor skill learning and execution.
[35] It has been observed in animal models that HD subjects had diminished CBP activity and decreased neuronal histone acetylation.
[22] Because the exact causes of the disease are not clearly understood, there are a number of different mechanisms by which CBP is hypothesized to play a role in the progression of AD.
In many cases of early-onset familial AD (FAD), there are mutations of the proteins that make up the enzyme responsible for the creation of Aβ plaques.
[16][22] Additionally, in mouse models of AD, it has been shown that there is a decrease in neuronal histone acetylation, a critical function of CBP.