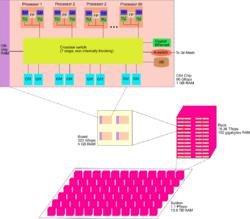
Cellular architecture
IBM's Cell microprocessor was the first cellular architecture to reach the market.
Cellular architecture takes multi-core architecture design to its logical conclusion, by giving the programmer the ability to run large numbers of concurrent threads within a single processor.
Speed-up is achieved by exploiting thread-level parallelism inherent in many applications.
Cellular architectures follow the low-level programming paradigm, which exposes the programmer to much of the underlying hardware.
This allows the programmer to greatly optimize their code for the platform, but at the same time makes it more difficult to develop software.