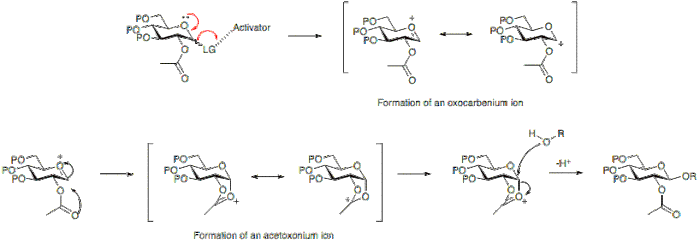
Chemical glycosylation
The reactions often result in a mixture of products due to the creation of a new stereogenic centre at the anomeric position of the glycosyl donor.
Alternatively, the absence of a participating group at position 2 allows for either attack from the bottom or top face.
Recently several research groups have shown these donors to have unique reactive properties and can differ from other glycosyl chlorides or bromides with respect to reaction time, efficiency, and stereochemistry.
[12] Iodide donors may typically be activated under basic conditions to give β-glycosides with good selectivity.
The advantage of using thioglycosides is their stability under a wide range of reaction conditions allowing for protecting group manipulations.
[13] O-Glycosyl trichloroacetimidates are prepared via the addition of trichloroacetonitrile (Cl3CCN) under basic conditions to a free anomeric hydroxyl group.
This can, however, be overcome by washing the organic layer with 1 M NaOH solution in a separatory funnel prior to chromatography.