Chiral auxiliary
In stereochemistry, a chiral auxiliary is a stereogenic group or unit that is temporarily incorporated into an organic compound in order to control the stereochemical outcome of the synthesis.
In addition, transformations with chiral auxiliaries tend to be versatile and very well-studied, allowing the most time-efficient access to enantiomerically pure products.
[2] Furthermore,[7] the products of auxiliary-directed reactions are diastereomers, which enables their facile separation by methods such as column chromatography or crystallization.
[5] The cycloaddition product was carried forward to the iodolactone shown below, an intermediate in the classic Corey synthesis of the prostaglandins.
[14] BINOL was also used as a chiral auxiliary to control the formation of a P-stereocenter in an asymmetric metal-catalyzed C-P coupling process.
Mondal et al. discovered that the Pd-catalysed C-P cross-coupling reaction between axially chiral BINOL-based phosphoramidites and aryl halides or triflates proceeds with excellent stereoselectivity due to the presence of BINOL near the reacting P center.
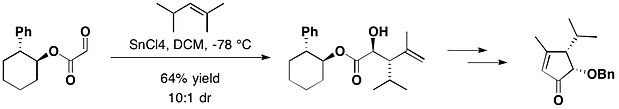
[16] In the total synthesis of (−)-heptemerone B and (−)-guanacastepene E, attached with trans-2-phenylcyclohexanol, the glyoxylate reacted with 2,4-dimethyl-pent-2-ene, in the presence of tin(IV) chloride, yielding the desired anti adduct as the major product, together with a small amount of its syn isomer with 10:1 diastereomeric ratio.
Deprotonation at the α-carbon of an oxazolidinone imide with a strong base such as lithium diisopropylamide selectively furnishes the (Z)-enolate, which can undergo stereoselective alkylation.
Soft enolization with the Lewis acid dibutylboron triflate and the base diisopropylethylamine gives the (Z)-enolate, which undergoes a diastereoselective aldol reaction with an aldehyde substrate.
In the total synthesis of manzacidin B, Ohfune group utilized camphorsultam to construct the core oxazoline ring asymmetrically.
In the presence of butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) used as a radical scavenger, a toluene solution of the adduct between geraniol and camphorsultam was heated in a sealed tube at 140 °C, to provide mainly the (2R,3S)-isomer as the major rearrangement product in 72% yield, securing the two contiguous stereocenters including the quaternary carbon.
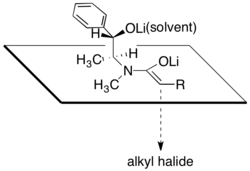
In accordance with this proposal, it has been observed that the diastereoselectivity of the alkylation step is highly dependent on the amount of lithium chloride present and on the solvent, tetrahydrofuran (THF).
Construction of quaternary carbon centers by alkylation of α-branched amide enolates is also possible, though the addition of DMPU is necessary for less reactive electrophiles.
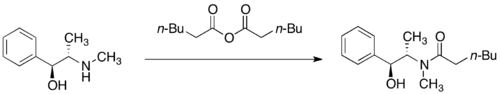
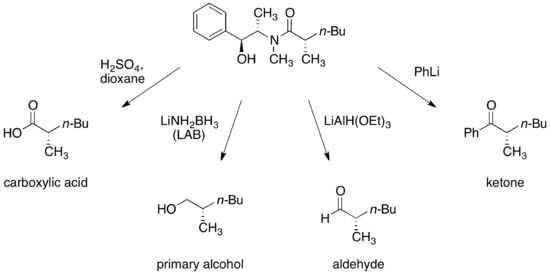
[30] Conditions have been developed for the transformation of pseudoephedrine amides into enantiomerically enriched carboxylic acids, alcohols, aldehydes, and ketones - after cleavage, the auxiliary can be recovered and reused.
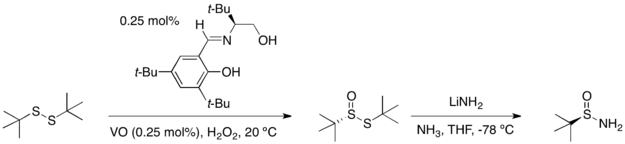
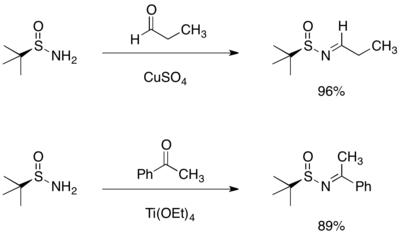
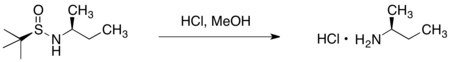
This specific sulfinamide chiral auxiliary was initially developed by Jonathan A. Ellman, and its use has been explored extensively by his group.
The observed stereoselectivity can be rationalized by a six-membered ring transition structure, wherein both oxygen and nitrogen of the sulfinyl imine coordinate magnesium.
Chiral auxiliaries are generally reliable and versatile, enabling the synthesis of a large number of enantiomerically pure compounds in a time-efficient manner.
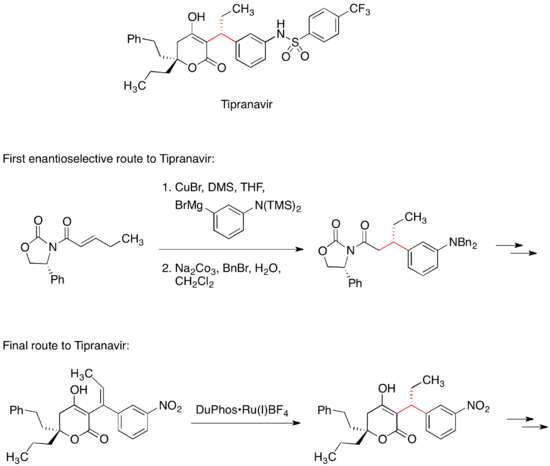
The first enantioselective medicinal chemistry route to Tipranavir included the conjugate addition of an organocuprate reagent to a chiral Michael acceptor.
The final, commercial route to Tipranavir does not feature a chiral auxiliary; instead, this stereocenter is set by an asymmetric hydrogenation reaction.
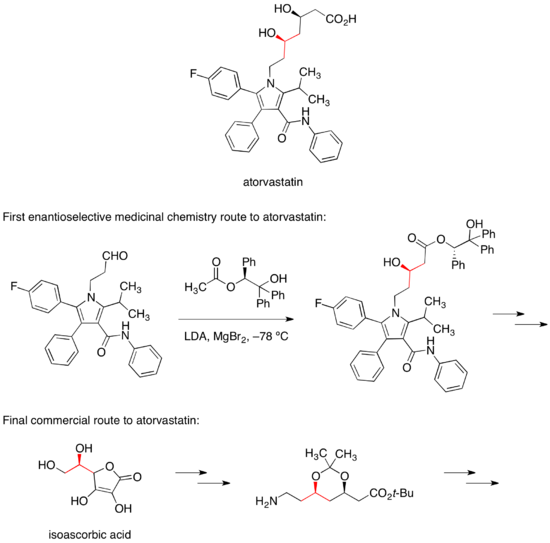
The first enantioselective medicinal chemistry route to atorvastatin relied on a diastereoselective aldol reaction with a chiral ester to set one of the two alcohol stereocenters.