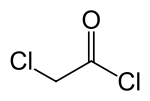
Chloroacetyl chloride
[3] It may be prepared from chloroacetic acid and thionyl chloride, phosphorus pentachloride, or phosgene.
The use of chloroacetyl chloride in the synthesis of lidocaine is illustrative:[5] The major use of chloroacetyl chloride is as an intermediate in the production of herbicides in the chloroacetanilide family including metolachlor, acetochlor, alachlor and butachlor; an estimated 100 million pounds are used annually.
Like other acyl chlorides, reaction with other protic compounds such as amines, alcohols, and water generates hydrochloric acid, making it a lachrymator.
There is no regulated permissible exposure limit set by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration.
However, the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health has set a recommended exposure limit at 0.05 ppm over an eight-hour work day.