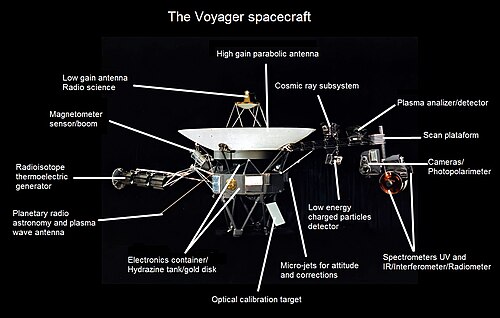
Cosmic Ray Subsystem
[1] As of 2019, CRS is one of the active remaining instruments on both Voyager spacecraft, and it is described by as being able to detect electrons from 3–110 MeV and cosmic ray nuclei 1–500 MeV/n.
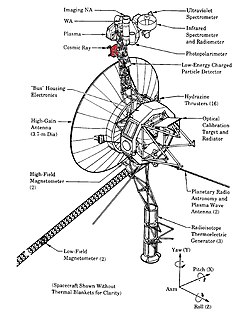
[7] CRS is one of the five fields and particle experiments on each spacecraft, and one of the goals is to gain a deeper understanding of the solar wind.
[9] In the summer of 2019, the heater for the CRS on Voyager 2 was turned off to save power, however, although it cooled off it was still returning data at a new lower temperature outside its original operating range.
[10] In 1977 the spectra of helium, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, and neon during the solar minimum was measured using the CRS instrument on the Voyagers that year.
[16] The solar minimum of 1977 occurred towards the end of year, and it was possible to observe both interplanetary, galactic, and anomalous energy spectra.
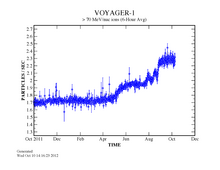
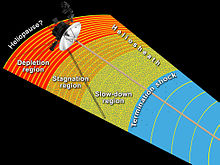
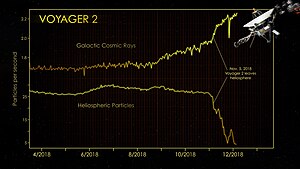
[27] First I don't think any of us on the CRS [Cosmic Ray Subsystem, an instrument on Voyager] team will ever forget watching on the computer monitors, even on an hourly basis, in one case, as some particle intensities dropped precipitously, and others increased simultaneously on several occasions in July and August, 2012.Other scientists proposed that this indicated a departure from the Solar System in the sense that it had left the Sun's heliosphere.
[26] The many revelations and restructured understandings as the Voyagers head out, as influenced by data from the CRS and other active instruments, was called by Nature publication as the "long goodbye".